
Of the six main asset classes, the one that stands out as perhaps the least understood is bonds. Although most people have a general idea of what bonds are and how they fit in an investment portfolio, they are incredibly complex financial instruments and misconceptions abound. I frequently hear people wonder if there is even any need to own them. So, let’s take a look and see if we can get a clearer picture of how bonds work and why they are useful.
Why do bonds exist?
Bonds are used by governments and corporations to raise capital. If a government issues a bond, it is borrowing money from the public to finance itself. Companies issue bonds so that they can expand operations or fund new business ventures. So if you buy a bond, you are loaning a government or a corporation money.
The key components of bonds
- Issuer: bonds can be issued by governments or corporations. Each issuer carries a different level of credit risk, with bonds issued by developed world governments considered the safest. Bonds from issuers with a lower credit rating carry more risk of default and pay a higher yield to compensate for that risk.
- Coupon rate: this is the annual interest rate paid to bondholders, expressed as a percentage of the bond’s face value. (often referred to as par value) So a bond with a $1,000 face value and a 5% coupon rate pays $50 a year in interest.
- Maturity date: bonds have a specified maturity date when the issuer repays the bond’s face value to the bondholder. Maturities can range from a few months to several decades, influencing the bond’s risk and potential return. A 30-year bond is regarded as more risky than a 5-year bond as more factors can affect the issuer’s ability to repay the debt over longer periods.
- Market price: the price of a bond in the secondary market can fluctuate based on changes in interest rates, credit quality and market demand. If the bond’s market value is higher than its face value, it is trading at a premium. If it is lower than face value, it is trading at a discount.
Understanding bond prices
Bonds can be bought and sold on the secondary market after they are issued. A bond’s value in this market is determined by its price and yield. The key thing to understand is that a bond’s price moves inversely to its yield. A bond’s price reflects the value of the income it can provide. So, if interest rates are falling, the value of older bonds that were sold in a higher interest rate environment increases and their price goes up. In a rising interest rate environment, older bonds become less valuable as investors would rather buy newer bonds paying higher yields.
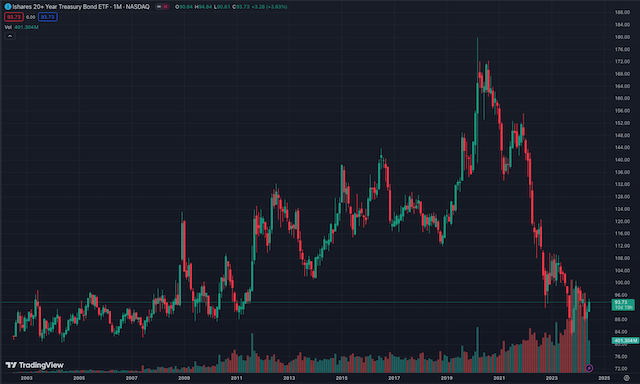
You can see this clearly in the performance of the above iShares TLT long-term treasury ETF. After the 2008 financial crisis, interest rates were kept low to stimulate economic recovery. Just as rates began to drift upwards, Covid happened and rates were slashed again. Bond prices increased significantly in this low interest rate environment and so the price of the ETF rose. When the Federal Reserve began raising interest rates in late 2021, bond prices fell heavily and continued to fall throughout the Fed’s tightening cycle, which is now nearing its end.
You could make a pretty strong argument that now is a good time to be buying a long-term treasury ETF like TLT. When the Fed begins cutting rates, bond prices will recover and investors will be able to capture capital gains along with income.
Conversely, having held interest rates low for longer than most other developed countries, Japan is now in a rising interest rate environment as the Bank of Japan attempts to slow down inflation. This means the price of Japanese Government Bonds is likely to fall.
Why own bonds?
Investors may choose to own bonds for a range of reasons. Those reasons include:
- Steady income – particularly applicable to retirees and investors who require income for other reasons
- Capital preservation – if held to maturity, bonds issued by institutions with strong credit ratings come with a low risk of loss of capital
- Portfolio diversification – bonds offer a good counterbalance to equity market volatility
- Capital appreciation – as above, bond prices can appreciate when central banks are cutting interest rates
- A hedge against economic downturn – in the US and Europe, inflation is cooling and economies are slowing. This means the income from bonds will be able to buy more goods and services, making bonds more attractive
How to buy bonds
For a typical retail investor, there is no need to buy individual bonds. Just like equities, investors can choose from a range of active or passive strategies offered by bond funds or bond ETFs. Generally, a passive ETF provides perfectly adequate exposure to bonds without any stress or hassle. For example, Blackrock’s iShares ETF series offers 135 different bond ETFs – more than enough to build a diversified bond allocation. The fixed income part of a well-diversified portfolio will generally contain a blend of shorter/medium/longer-term government bonds along with an allocation to more risky corporate and emerging market bonds.
Be sure to pay attention to your base currency when you build such a portfolio. If you are planning to spend the money in the UK eventually, you should be looking at UK Gilts as the core of your bond holdings rather than US treasuries. Don’t be afraid to engage professional help if you are not comfortable organising this yourself.
As to whether owning bonds is really necessary or not, that’s obviously an individual call to make. I would comment that if you are young and just getting started with investing a little money every month, averaging 100% into equity ETFs is a perfectly acceptable strategy for the first few years.
However, after you have been investing for some time and have built up a larger pool of capital, it is probably time to start thinking about diversifying into other asset classes to protect against sharp drawdowns in equity markets. Bonds become a useful tool as you shift from an aggressive capital accumulation strategy to a more balanced portfolio that offers growth and income with a degree of capital preservation.
Hopefully, this post goes some way to explaining what bonds are, how they work and the benefits of investing in them. Feel free to comment or send questions any time!
Disclaimer: This should go without saying, but the information contained in this blog is not investment advice, or an incentive to invest, and should not be considered as such. This is for information only.

